Jaggery, a traditional sweetener derived from sugarcane or palm sap, has been treasured for centuries not only for its delightful flavor but also for its myriad health benefits. From enhancing digestion to boosting immunity, jaggery offers a wealth of wellness advantages that make it a valuable addition to any diet. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the incredible health benefits of jaggery, shedding light on its nutritional profile, therapeutic properties, and versatile culinary uses.
Understanding Jaggery: Nature’s Sweet Secret
Jaggery, also known as “gur” in Hindi, is a natural sweetener made by boiling sugarcane juice or palm sap until it solidifies into a concentrated form. Unlike refined sugar, which undergoes extensive processing and bleaching, jaggery retains its natural nutrients and minerals, making it a healthier alternative to white sugar.
Nutritional Profile of Jaggery
Jaggery is rich in essential vitamins and minerals, including:
- Iron: Jaggery is a significant source of iron, making it beneficial for individuals with iron deficiency anemia.
- Calcium: Calcium in jaggery promotes bone health and helps maintain optimal bone density.
- Magnesium: Magnesium supports muscle function, nerve health, and energy production.
- Potassium: Potassium aids in regulating blood pressure and maintaining electrolyte balance.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus contributes to bone health, tissue repair, and energy metabolism.
- Vitamin B Complex: Jaggery contains various B vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), and B6 (pyridoxine), which play vital roles in metabolism and energy production.
Health Benefits of Jaggery
- Boosts Immunity: Jaggery is packed with antioxidants and minerals like zinc and selenium, which help strengthen the immune system and defend the body against infections and diseases.
- Improves Digestion: Consuming jaggery after meals can aid digestion by stimulating the secretion of digestive enzymes and facilitating the breakdown of food. It also helps prevent constipation and promotes regular bowel movements.
- Provides Energy: Jaggery is a natural source of carbohydrates and glucose, providing a quick and sustainable energy boost. It is often consumed by athletes and individuals engaging in strenuous activities to replenish glycogen stores and combat fatigue.
- Detoxifies the Body: Jaggery acts as a natural cleanser for the body, helping to flush out toxins and impurities from the bloodstream, liver, and digestive tract. Its alkaline nature helps maintain the body’s pH balance and promotes overall detoxification.
- Supports Respiratory Health: Jaggery is often used in traditional remedies for respiratory ailments like coughs, colds, and asthma. Its anti-inflammatory and expectorant properties help soothe the respiratory tract and alleviate symptoms of respiratory disorders.
- Regulates Blood Sugar: Despite being a sweetener, jaggery has a lower glycemic index than refined sugar, meaning it causes a slower and steadier rise in blood sugar levels. This makes it a suitable option for individuals with diabetes when consumed in moderation.
- Enhances Skin Health: The antioxidants and minerals present in jaggery help promote healthy skin by combating free radical damage, preventing premature aging, and improving skin elasticity. It also aids in maintaining a clear complexion and reducing acne and blemishes.
- Alleviates Menstrual Symptoms: Jaggery is often recommended for women experiencing menstrual discomfort due to its iron-rich content, which helps alleviate symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and mood swings associated with menstruation.
Culinary Uses of Jaggery
Jaggery lends its unique flavor and sweetness to a wide array of culinary creations, including:
- Sweet Treats: Jaggery is commonly used in desserts, confections, and sweets like laddoos, halwas, and chikkis.
- Beverages: It can be dissolved in hot water or milk to make delicious beverages like jaggery tea or spiced milk.
- Sauces and Dressings: Jaggery syrup is used as a sweetener in sauces, dressings, and marinades for savory dishes.
- Baked Goods: Jaggery can be substituted for sugar in baking recipes to impart a rich, caramel-like flavor to cakes, cookies, and bread.
Tips for Choosing and Storing Jaggery
When purchasing jaggery, opt for organic varieties that are free from additives, preservatives, and chemical contaminants. Look for jaggery that is dark brown or caramel in color, as this indicates higher mineral content and purity.
Calorie Count and Nutritional Value of Jaggery
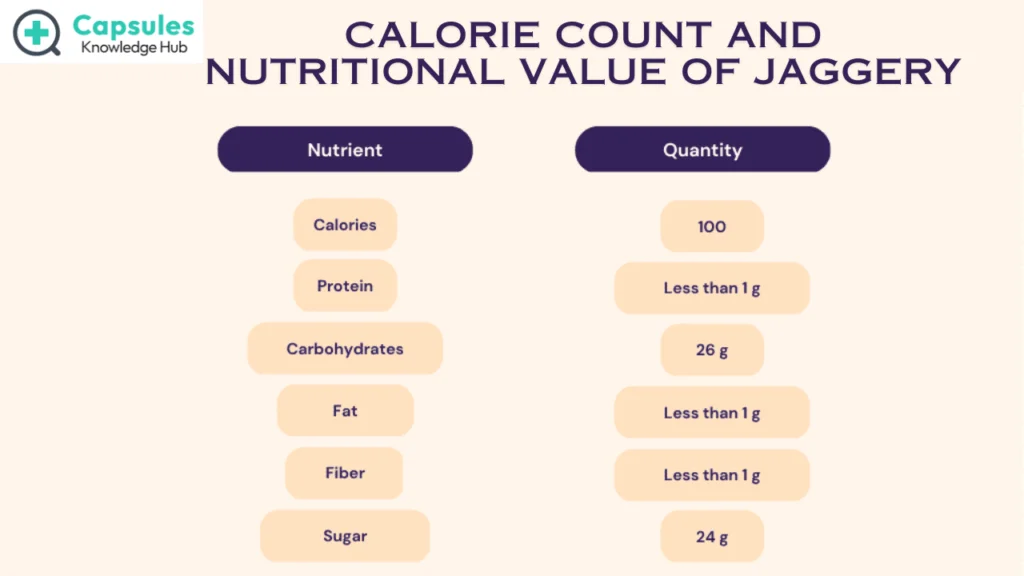
Jaggery is a super sweetener made from sugarcane juice and palm sap. It is known by various names in different parts of the world. In India, it is known as “Gud,” in South America and Latin American countries as “Panela,” in Japan as “Kokuto,” in Brazil as “Rapadura,” and as “Hakura” in Sri Lanka. There may be differences in the world among the names of jaggery, but there is one common connotation related to jaggery: it is considered a healthy food with rich nutritional value. Below is the nutritional value chart for jaggery:
NUTRITIONAL VALUE OF JAGGERY
| Nutrient | Amount per 100 grams |
| Carbohydrates | 97 gram |
| Fat | 0.1 gram |
| Protein | 0.4 gram |
| Fiber | 0.6 gram |
| Phosphorus | 20-90 mg |
| Iron | 10-13 mg |
| Calcium | 40-100 mg |
| Sucrose | 65-85 gram |
| Vitamin C | 7 mg |
| Vitamin A | 3.8 mg |
| Vitamin E | 111.3 mg |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.01 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.06 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.01 mg |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.01 mg |
| Potassium | 10-56 mg |
| Magnesium | 70-90 mg |
| Zinc | 0.2-0.4 mg |
| Copper | 0.1-0.9 mg |
| Sodium | 19-30 mg |
CALORIE COUNT OF JAGGERY
The calorie count of 100 grams of jaggery is 383 kcal, which means you will get 383 kcal of energy by eating 100 grams of jaggery.
7 Health Benefits of Eating Jaggery
PROVIDES VITAL NUTRIENTS
According to the good health organic blog “Jaggery with incredible health benefits”, jaggery is a superfood that provides numerous vital nutrients to the human body. Jaggery is a rich source of carbohydrates and sucrose. Iron, calcium, and phosphorus are also found in significant amounts in jaggery. Jaggery is also a source of vitamins, although it has a lesser amount of vitamins in it. Still, it is a great source of vitamin A.
Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, B2, B5, and B6. There are some amounts of fiber, protein, and fat also found in jaggery. Overall, a great alternative to get vital nutrients if you lack a balanced diet.
IMPROVES METABOLIC HEALTH
Jaggery is a great option for improving your digestive health; it helps in the activation of digestive enzymes and helps in bowel movement in our body, which helps in digestion. Because of its blood sugar-regulating properties and fiber-rich content, jaggery plays a crucial role in improving digestion. Therefore, adding jaggery to your diet boosts your metabolism & aids digestive health, and keeps your insulin levels in check.
HELP IN THE AID OF ANEMIA
Jaggery is a great option for anemia patients to treat their disease. Jaggery is an excellent source of iron making it a great remedy for anemic people. Anemia is a disease where individuals suffer from deficiencies of hemoglobin, and for hemoglobin production, the human body needs iron, and jaggery is a great source for adding iron to your diet. Hence, it helps in the treatment of anemia.
PREVENTS RESPIRATORY AILMENTS
Jaggery is a great option to prevent respiratory problems. Jaggery is high in magnesium, and magnesium helps the bronchial muscles in our body relax and strengthen themselves and these muscles are vital for balanced breathing. This is why jaggery is known for preventing many respiratory problems like coughs, colds, allergies, and lung or throat infections. For better benefits, mix it in warm milk or make a tea with jaggery.
What is Jaggery?
Definition and Description

Wellhealthorganic.Com:Jaggery-With-Incredible-Health-Benefits
Jaggery is an unrefined sugar product derived primarily from sugarcane and palm. It is produced by boiling down the juice of these plants until it solidifies into a dense, brown block or granules. Unlike refined white sugar, jaggery retains many of the natural nutrients found in the original plant material, including minerals like iron, potassium, and magnesium. Its color can range from golden yellow to dark brown, depending on the source and method of production.
History and Cultural Significance
The history of jaggery dates back thousands of years, with its origins deeply rooted in ancient Indian and African cultures. It has been used not only as a sweetener but also as a medicinal ingredient and a significant part of various cultural rituals and celebrations. In India, jaggery (known locally as “gur”) is often used in religious offerings and festive foods, symbolizing sweetness and auspiciousness. Similarly, in Africa, it plays a crucial role in traditional ceremonies and daily diets.
Comparison with Other Sweeteners
When compared to other sweeteners, jaggery stands out due to its natural production process and rich nutritional profile. Unlike white sugar, which undergoes extensive refining and bleaching, jaggery is made using traditional methods that preserve its beneficial properties. It also contains more complex carbohydrates and is digested more slowly, providing a steady release of energy without the rapid spikes and crashes associated with refined sugar.
Types of Jaggery
Sugarcane Jaggery

Sugarcane jaggery, the most common type, is made by boiling sugarcane juice until it thickens and solidifies. It has a distinct, earthy flavor and a rich brown color. This type of jaggery is widely used in Indian cuisine, both in sweet dishes and as a natural sweetener for beverages.
Date Palm Jaggery
Date palm jaggery, also known as “khajur gur,” is derived from the sap of date palm trees. It is particularly popular in the Middle East and North Africa, where it is used in traditional desserts and sweets. Date palm jaggery has a unique, slightly smoky flavor and is often considered a delicacy.
Coconut Jaggery
Coconut jaggery, or “gur nariyal,” is made from the sap of coconut palm trees. This variety is commonly used in South Indian and Southeast Asian cuisines. It has a light, caramel-like flavor and is often used in sweets and beverages.
Differences and Similarities
While all types of jaggery share the common trait of being unrefined and nutrient-rich, they differ in flavor, color, and texture due to the source of their sap and the methods used in their production. Sugarcane jaggery tends to be denser and darker, while date palm and coconut jaggery have lighter flavors and colors. Despite these differences, all types of jaggery offer similar health benefits, making them excellent natural sweeteners.
Nutritional Profile of Jaggery
Macronutrients in Jaggery
Jaggery is composed mainly of carbohydrates, with a small amount of protein and virtually no fat. A typical 100-gram serving of jaggery provides approximately 380 calories, making it a significant source of energy. The carbohydrates in jaggery are complex, providing a slow and steady release of energy, which helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Vitamins and Minerals
Jaggery is rich in essential vitamins and minerals that are often stripped away during the refining process of white sugar. It contains notable amounts of iron, which is crucial for maintaining healthy blood levels and preventing anemia. Additionally, jaggery provides magnesium, potassium, and calcium, all of which are vital for various bodily functions, including muscle function, bone health, and cardiovascular health.
Comparison with Refined Sugar
When compared to refined sugar, jaggery offers a more robust nutritional profile. Refined sugar provides empty calories with no significant vitamins or minerals, while jaggery supplies not only energy but also important nutrients. This makes jaggery a more healthful option for those looking to satisfy their sweet tooth without compromising their nutritional intake.
Health Benefits of Jaggery
Boosts Immunity

Jaggery is packed with antioxidants and minerals that help strengthen the immune system. The presence of selenium and zinc in jaggery helps combat oxidative stress and free radical damage, enhancing the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Aids Digestion
Regular consumption of jaggery can aid in digestion by stimulating the secretion of digestive enzymes. It also acts as a mild laxative, helping to relieve constipation and promoting regular bowel movements.
Detoxifies the Liver
Jaggery acts as a natural detoxifier, helping to cleanse the liver by flushing out harmful toxins. This is primarily due to its high antioxidant content, which supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes.
Improves Skin Health
The antioxidants and minerals in jaggery can improve skin health by preventing oxidative damage and promoting a healthy complexion. Regular consumption of jaggery can help reduce acne, pimples, and other skin problems.
Prevents Anemia
Due to its high iron content, jaggery is an effective natural remedy for preventing anemia. It helps increase hemoglobin levels in the blood, ensuring adequate oxygen transport throughout the body and preventing fatigue and weakness.
Regulates Blood Pressure
Jaggery contains potassium and sodium, which help maintain the balance of electrolytes and regulate blood pressure. This makes it beneficial for individuals with hypertension or those looking to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Jaggery and Immunity
How Jaggery Boosts the Immune System
Jaggery’s role in boosting immunity is primarily attributed to its rich content of antioxidants, minerals, and vitamins. The antioxidants present in jaggery, such as phenolic compounds, help combat free radicals that can cause cellular damage and weaken the immune system. Additionally, minerals like zinc and selenium enhance immune function by supporting the activity of immune cells and reducing oxidative stress.
Role of Antioxidants in Jaggery
Antioxidants are compounds that protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation. Jaggery is a natural source of these compounds, which help in neutralizing free radicals. This not only strengthens the immune system but also reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. Regular consumption of jaggery ensures a steady supply of these beneficial antioxidants.
Benefits During Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes often bring about a surge in common illnesses like colds, coughs, and flu. Consuming jaggery during these times can provide an added boost to the immune system, helping the body fend off infections more effectively. Its warming effect on the body also makes it a popular choice in winter, providing relief from cold-related ailments.

